Digital & Embedded Systems
Example CPU's
CPU 1 - A very basic CPU. It is composed of the four basic CPU elements, the ALU, the CU, the memory store and the clock which provides the phase control. Notice that there is no branching available for this CPU. Therefore, the program written in the ROM executes the same way each time. This CPU also lacks the ability to write data back to the memory store.
pc = pc + 1 NOP acc = NOT acc
pc = pc + 1
NOT acc = acc AND constant
pc = pc + 1
AND constant acc = acc OR constant
pc = pc + 1
OR constant acc = acc + constant
pc = pc + 1
ADD constant acc = constant
pc = pc + 1
LOAD constant Nothing N/A Nothing N/A
CPU 2 - This CPU is an extention of the basic CPU 1. Two important features are added to make this CPU a basic model of the von Neumann architecture. The first feature is the ability to write data back to the memory store using op-code 6. The second feature is the conditional branch by selecting op-code 7.
pc = pc + 2 NOP acc = NOT acc
pc = pc + 2
NOT acc = acc AND memory
pc = pc + 2
AND memory acc = acc OR memory
pc = pc + 2
OR memory acc = acc + memory
pc = pc +2
ADD memory acc = memory
pc = pc +2
LOAD memory memory = acc
pc = pc + 2
STORE acc < acc unchanged >
if acc = 0 then pc = pc + address
else pc = pc + 2
BEQ address
CPU 3 - This CPU adds even more functionality. With this CPU, operations can be performed on either values at memory locations or directly on the values stored in the address register. This CPU also includes an unconditionaly break to an address.
acc = constant
pc = pc + 2
LOAD constant acc = memory
pc = pc + 2
LOAD memory memory = acc
pc = pc + 2
STORE memory acc = acc + memory
pc = pc +2
ADD memory acc = acc AND memory
pc = pc + 2
AND memory < acc unchanged >
if acc = 0 then pc = pc + address
else pc = pc + 2
BEQ address < acc unchanged >
pc = pc + address
BRA address acc = NOT acc
pc = pc + 2
NOT
CPU 4 - A complicated CPU which can perform operations on memory or constants. Notice that the interesting feature of this CPU is that the same set of operations can be performed with a value from a memory location or a constant stored in the address register.
acc = memory
pc = pc + 2
LOAD memory memory = acc
pc = pc + 2
STORE memory acc = NOT acc
pc = pc + 2
NOT acc = acc + memory
pc = pc + 2
ADD memory acc = acc - memory
pc = pc + 2
SUB memory acc = acc AND memory
pc = pc + 2
AND memory acc = acc OR memory
pc = pc + 2
OR memory < acc unchanged >
if acc = 0 then pc = pc + address
else pc = pc + 2
BEQ address acc = constant
pc = pc + 2
LOAD constant N/A N/A N/A N/A acc = acc + constant
pc = pc + 2
ADD constant acc = acc - constant
pc = pc + 2
SUB constant acc = acc AND constant
pc = pc +2
AND constant acc = acc OR constant
pc = pc +2
OR constant < acc unchanged >
pc = pc + address
BRA address
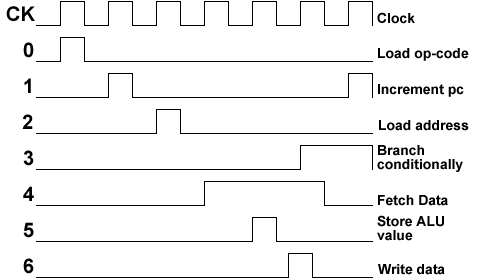
CPU 4 Timing Cycle - The timing cycle that the pulse generator and clock generate.